
SPSS CODE IF SYNTANTX LICENSE
SPSS from managed desktop application store and other Network Installations use the license server so you won't need to bother with annual codes.
SPSS CODE IF SYNTANTX UPDATE
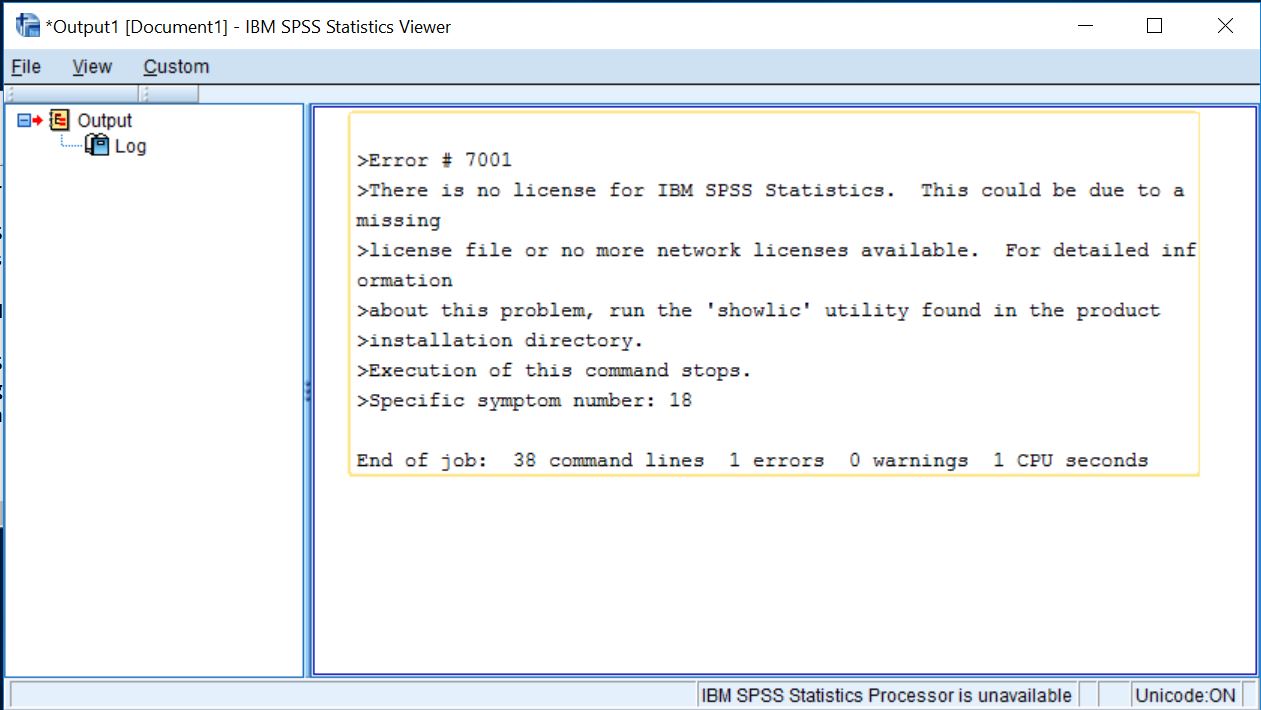
Below is an example of the output for the Gender syntax sub-file after using the CD and INSERT Commands.If you do a manual Site License installation of SPSS or need to update your annual license, you will need a current authorization code to activate it.Įvery year after that in September you will need to enter a new code authorize the software for the next academic year, if you are not using the license server. The output does look slightly different, but will still show errors and note any issues like normal. When the main syntax file is run, it will open and run all the syntax sub-files. If you did not direct it to a folder using the CD command first, each INSERT FILE command would require the entire path of the file location to be included every time, such as: INSERT FILE=’P:\SPSS Syntax Library\Variables\Gender.sps’. The CD command directs SPSS to a specific folder which is followed by a list of the INSERT FILE commands for each syntax sub-file, including the one for Gender. The syntax shown above is a small part of the main syntax file for large standardized data file. An example of the CD command is shown in the first line in the syntax below (note how it matches the file path of the folder as shown circled in the window above). If you are inserting multiple sub-files that are stored in the same folder, you can shorten the file path to just the file name by first including the CD command which changes the working directory location, or in other words, directs SPSS to look in a specific folder where the files will be. The INSERT command is written in syntax as:

Below is an example of the folder and location where the Gender sub-file among many others are stored. In general, it is useful to have a single location, such as a shared folder, to create your “Syntax Library” of syntax sub-files. This syntax sub-file labels both the variable Gender and its current values, and then creates two derived variables (D_Gender_MF and D_Gender_MFU) to provide other ways of grouping Gender. In the example below of a sub-file for the variable Gender, I also include documentation to explain what variable(s) is used from the data file, the data dictionary number for the variable(s) (if applicable), what the syntax in the sub-file does (creates labels, derives variables, etc.), the data files that will be using this syntax, and file creator with date created or last updated. birth month, day, year) that are always found together. It is often best if the syntax sub-file (the name I use for the syntax file to be run within another file) is used to work on one variable or a related group of variables (e.g. Before using the INSERT command, some work does need to be done to make sure the name and format of the variables used in the inserted syntax are standardized across all data files with which you plan to use. birthdate, race, or major) are included in multiple data files. The INSERT command is useful to eliminate duplicated syntax and maintain standardized names, labels, and/or commonly derived variables when some of the same variables (e.g. Instead of duplicating the syntax in the syntax file for each data file, a smaller syntax file that only labels a variable and its values, for example, can be saved and then run by other syntax files with the INSERT command in SPSS. There are usually some of the same variables (gender, birthdate, etc.) included in multiple data files that your office collects or maintains.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
